-
 Richard Berry
Richard Berry
- Updated
Futures brokers let you speculate on the financial markets going up or down with the safety of on exchange standardised futures contracts.
Good Money Guide has ranked and reviewed the best futures brokers in the UK to help you choose the most appropriate account for your futures trading strategy.
Best UK Futures Brokers Compared
| Futures Broker | Markets | Exchanges | Min Deposit | Commission | GMG Rating | More Info |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 330+ | 35 | £2,000 | $0.25-$0.85 per lot | Visit Broker | |
 | 100+ | 5+ | £100 | $0.49-$0.89 | Visit Broker | |
 | 300+ | 20 | £1 | $4-1 per lot | Visit Broker |
Our Picks Of The Best Futures Brokers In The UK
❓Methodology: Good Money has rounded up the best futures brokers based on:
- 17,000 customer votes in our annual awards
- Our review team’s experiences testing the platforms with real money
- A deep-dive into the features that make them stand out compared to alternatives
- Our exclusive interviews with the trading platform CEOs and senior management
Find out more about how we review future brokers and other financial providers in our How We Rate page.
Interactive Brokers: Best Futures Broker Overall
🏆Award Winner🏆

- Futures markets available: 330+
- Futures exchanges: 35
- Minimum deposit: £2,000
- Commissions: $0.85-0.25 per lot
62.5% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider
Interactive Brokers won “best futures broker” in our 2023 awards as they provide very low trading costs, and institutional-grade futures trading platform and wide market access.
Interactive Brokers offer one of the best futures trading platforms in the UK for both simple and complex trading strategies. Overall, Interactive Brokers is the cheapest major brokerage offering futures trading so is suitable for traders looking for discount execution from a well-established and capitalised company.
Interactive Brokers Review

Name: Interactive Brokers
Description: Interactive Brokers is a major US online automated electronic broker company. The financial broker is listed on the Nasdaq Exchange with ticker IBKR. The firm operates in 150 electronic exchanges in 33 countries, and offers trading in 23 currencies. Interactive Brokers has more than 1.75 million institutional and retail customers.
Why we like them
Interactive Brokers is an exceptional trading platform that offers institutional-grade trading capabilities to private clients around the world. IBKR has some of the lowest trading and investing fees and the widest market range in the industry.
Pros
- Very low dealing fees
- Wide market range
- Direct market access
- Complex order types
Cons
- Customer services can be slow
-
Pricing
(5)
-
Market Access
(5)
-
Apps & Platform
(5)
-
Customer Service
(3)
-
Research & Analysis
(5)
Overall
4.6Plus500: Futures Trading For US Residents
- Futures markets available: 100+
- Futures exchanges: 5
- Minimum deposit: $100
- Commissions: $0.49-$0.89 lot
80% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider.
Plus500 is based in the UK, but for US residents it offers futures trading instead of CFDs.
Plus500 US Futures Trading Review

Name: Plus500 US
Description: Plus500 is an online trading company that operates in more than 50 countries globally. Founded in 2008, it has more than 26 million customers worldwide today. Plus500 is headquartered in Israel, however, it’s listed in the UK on the London Stock Exchange. In the US, its platform is operated by Plus500US Ltd, which is licensed to offer the trading of futures via Plus500US Financial Services LLC, a Futures Commission Merchant that is registered with the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and is a member of the National Futures Association (NFA).
Is Plus500 a good futures broker?
Yes, Plus500 is an online trading company that operates in over 50 countries worldwide and in the US, its platform allows you to trade futures on a range of assets. Plus500 also offers a range of features designed to help traders capitalize on opportunities in the markets including charting tools and real-time news feeds. There is a demo account for those looking to learn how to trade futures before committing real money, but one downside is that there are some platforms that offer more futures markets than Plus500.
Pros
- You can trade a range of instruments and assets including equity indexes, crypto, and commodities.
- You can start trading with a small amount of capital.
- There is a demo account for beginners.
Cons
- With Plus500 US, you can only trade futures. You can’t buy stocks or funds directly.
- There is no telephone customer service available.
- Plus500 doesn’t offer as many futures as some other platforms do.
-
Pricing
(4)
-
Market Access
(4)
-
App & Platform
(4)
-
Customer Service
(4)
-
Research & Analysis
(4)
Overall
4Saxo Markets: Excellent Futures Trading Platform For Professional Traders
- Futures markets available: 300+
- Futures exchanges: 20
- Minimum deposit: £1
- Commissions: $4-1 per lot
65% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider
Saxo Markets won “best futures broker” in our 2022 awards as they offer a very robust futures trading platform, dedicated dealers and low costs. Overall Saxo Markets offer the best futures trading platform for the majority of semi-professional and institutional traders in the UK. They also offer access to the markets via CFDs and options for traders that want a more rounded service as well as investment options like physical shares dealing and investment bonds.
Is Saxo good for futures trading?
Yes, Saxo is one of the best futures brokers we compare. I would say their major competitor for futures trader is Interactive Brokers, which is much cheaper, but Saxo offers a better personal service. Smaller retail brokers like Plus 500 are moving into the futures trading industry (as opposed to CFDs) but that is only to capture the US market. One key advantage of Saxo is that they are one of the few TradingView brokers that let you execute trades as DMA futures.
Saxo Review

Name: Saxo
Description: Saxo is one of the largest CFD brokers worldwide and provides direct market access to equities, bonds, forex, futures and options as well as being a major liquidity and infrastructure provider to wealth managers, banks and smaller brokers.
65% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider
Is Saxo Markets a good broker?
Yes, Saxo is a good choice for more sophisticated traders. The platform, analysis, and direct market access may be too complicated for beginners. But, for experienced traders its coverage, commissions and research are unrivalled.
Pros
- Direct market access
- Low commissions
- Robust trading platform
Cons
- Seen as a trading platform for professionals
-
Pricing
(4.5)
-
Market Access
(4.5)
-
Online Platform
(5)
-
Customer Service
(4.5)
-
Research & Analysis
(4.5)
Overall
4.6What Is A Futures Broker?
Futures brokers provide direct market access to futures exchanges so their clients can trade futures contracts. When trading futures, traders buy and sell futures contracts that give them the obligation to buy or sell a set amount of a specific asset at a specific date in the future.
All futures brokers in the UK must be regulated by the FCA. You can check the status of what a futures broker is regulated to do on the FCA register. Most futures brokers will have an office or exposure to the London futures markets, as the UK offers one of the most robust financial infrastructures for trading futures.
Pros
- Futures contracts have very low margin
- Futures contracts are on-exchange which reduces counter-party risk
- The cost for trading futures are very low for high-volume traders
Cons
- Some brokers may insist clients close positions before delivery
- Trade in lots of preset amounts that are inflexible for exact accounting
- Mainly traded on US-based exchanges and are USD-denominated
- They trade in large amounts that cannot be partially closed
- You need to be a professional trader to get the full benefits
How To Choose A Futures Broker
The main things to consider when choosing a futures broker are:
- Are they right for your level of experience?
- How many futures exchanges are they connected to?
- What are their commissions and fees?
- Do they offer any other account type other than futures?
- What added value does the broker offer?
What Is The Best Futures Broker For Beginners?
Saxo Markets is a good choice for new futures traders as their web-based platform is very easy to use. Use our comparison tables of what we think are the best futures brokers to compare commission, market access and what different types of accounts they offer.
| Beginner Features: |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trading Signals | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Webinars | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Seminars | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Leverage Control | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Low-Risk Products | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Investment Account | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Mini Contracts | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Micro Contracts | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Futures trading is a high-risk form of speculation and not suitable for complete beginners. If you are a beginner and looking for a futures broker, these are the main things you consider:
- Do you fully understand the risks?
- Do you have enough risk capital to diversify your exposure?
- If you do not have the relevant experience, you will be classified as a retail client and not allowed to trade futures
- If you can demonstrate the relevant experience, you will be classified as a professional trader and your futures broker will not be obliged to explain how the markets work, and you will lose some of the protection the FCA offers retail traders.
What Is The Best Futures Broker For Advanced & Professional Traders?
Interactive Brokers is a good choice for experienced futures traders as their fees are very low for high frequency trading. IBKR also has a huge range of execution types for algo trading and API strategies.
| Advanced Features: |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voice Brokerage | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Corporate Accounts | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Level-2 | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Algo Trading | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Prime Brokerage | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
The majority of UK futures brokers require clients to be classified as professional and have a clear understanding of the risks and mechanics of futures trading before they can have an account. The UK regulator, the FCA, requires all clients to either be classified as retail, professional, or ECP (Exchange Counter Parties).
Retail clients tend to trade more accessible products such as financial spread betting or CFDs through a CFD broker, which often require smaller trade sizes. Futures brokers in the UK have their margin and trade size levels set by the underlying futures contracts, and the margin is set by the exchanges where the futures are traded.
Which Futures Trading Platforms Offer Voice Brokerage (Phone Dealing)?
Saxo Markets lets you trade futures over the phone. All futures brokers offer online futures trading through either their own propriety trading platform or third-party platforms. Most futures trading is done online through futures brokers, although there is still demand for telephone-based futures broking, known as voice brokerage. Our comparison table of online futures brokers in the UK highlights which brokers offer voice and online trading, as well as prime and API access.
Which Is The Best Futures Broker For Scalping?
Interactive Brokers is the best futures broker for scalping because they charge the lowest commission. They also have an excellent order execution tool that lets you trade the market as a percentage of volume, automatically entering and pulling orders. The best futures brokers for scalping will offer direct market access to the futures exchanges, so traders can work orders inside the market prices.
Scalping is a type of trading where futures traders buy and sell quickly with the intention of taking advantage of small moves in bid-offer prices.
Traders that are planning on scalping should inform their brokers of this so that they can negotiate lower trading costs, as the lower the cost of trading futures, the higher the returns on a scalping trading strategy will be. You can read more on why some brokers don’t allow scalping here.
Which Is The Best Futures Broker For Mini & Micro Lot Trading?
Tickmill provides an excellent range of micro contracts for futures traders who want to start small. e-Micro futures are mini versions of full-size futures contracts. They were introduced to allow futures traders to have more control over their exposure by trading in small contract sizes.
They are particularly helpful for smaller futures traders or beginners, as e-mini futures contracts require a lower margin and have less exposure to the markets. Due to their popularity over full size futures contracts, they are also more liquid contracts and are therefore more accessible to trade.
For example, the full-size S&P 500 futures contract is worth $250 times the S&P 500 index, whereas the e-mini S&P 500 futures contract is worth $50 times the S&P 500 index.
What Is The Best Future Broker For US Citizens?
Our analysis shows that Interactive Brokers is the best futures broker in the US. Even though Saxo Markets has won the award for best futures broker more often, Saxo Markets is not able to take on US clients. However, Saxo Markets can offer futures trading on US products to non-US residents.
US futures traders are not allowed to trade futures through a UK-based futures broker. US regulations require that US residents trade futures through US futures brokers.
However, most UK-based futures brokers will have an office in the US and our comparison tables will redirect users to US futures broker entities if they are based in the US. UK futures traders are allowed to open futures trading accounts with US brokers.
As with the UK, the criteria for determining the best US futures brokers are the same. However, in the US, as there are no other derivatives products like spread betting or CFD trading, private (retail) traders are more likely to trade futures and options as a way to get leveraged exposure to the financial markets.
⚠️ FCA Regulation
All futures trading platforms that operate in the UK must be regulated by the FCA. The FCA is the Financial Conduct Authority and is responsible for ensuring that UK futures brokers are properly capitalised, treat customers fairly and have sufficient compliance systems in place.
Good Money Guide only features futures platforms that are regulated by the FCA, where your funds are protected by the FSCS.
Futures Trading Explained
👉 Futures are a financial contract where a commodity or financial instrument is bought or sold for a fixed price at a certain date
👉 Futures can be futures on stock indexes, commodities, precious metals and US Treasury (e.g. bonds)
👉 Futures can be traded at a futures market like the New York Mercantile Exchange.
What Are Futures?
Futures are a type of financial contract. They are agreements that mean the buyer has to purchase, or seller has to sell, an asset on a specific date at an agreed price. That asset might be an index, currency, or commodity a treasury (interest rate).
The idea is to let people hedge exposure and speculate (and hopefully profit on) price movements. For the buyer, the future means they can lock in a price (so not having to worry about fluctuations). Whilst for the seller, they can ensure future sales at a given price.
What Is Futures Trading?
Futures trading is entering into a contract to buy or sell a given instrument at a set price and a set date in the future.
This could be oil, gold, FTSE, DAX or bonds and be a month or year ahead. Futures trading is used for both hedging and speculation and is a very important component of today’s global marketplace.
How Does Futures Trading Work?
When you trade futures you are trading the price of an underlying instrument or commodity on a future date.
Futures trading platforms access futures exchanges to match buyers and sellers. For example, farmers with crops to sell and food manufacturers with ingredients to buy, both sides would like to get and lock in the best price they can. Through futures markets, farmers can sell crops they have yet to harvest and food manufacturers can secure supplies and fix their costs.
Futures markets are exchange-traded and usually, have a central counterparty or clearinghouse that acts as buyer to all sellers and the seller to all buyers. This is effectively guaranteeing the settlement of all trades conducted on the exchange. Many futures contracts are deliverable though there are also a growing number of CFDs or contracts for the difference which are settled for cash and not the underlying instrument or commodity.
- Related guide: 50 rules for successful trading
Futures trading takes place on a margined basis with an initial margin or deposit required at the outset of the trade and then variation or maintenance margin as required throughout the lifetime of the trade. These margins are pledged to the clearinghouse or central counterparty.
What is A Futures Market?
A futures market is a marketplace where futures contracts are traded. The vast majority are electronic (and therefore open 24/7). These include the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) and the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). Futures markets allow buyers and sellers to access clearing houses – basically ‘middlemen’ of the trade.
What Can You Trade With Futures?
You can trade on a wide range of things. The most popular markets for futures trading are:
- Indices
- Foreign exchange
- Commodities
- Treasuries
There are futures markets on all sorts of different products ranging from cheese to short-term interest rates and carbon emissions. What’s more new contracts are regularly introduced, for example, we have recently seen the launch of Bitcoin futures contracts on a cryptocurrency for crypto trading and environmental sustainability.
How To Start Futures Trading
To start trading futures you need a futures broker, a thorough understanding of the financial markets and some risk capital (money).
When choosing a futures trading platform you want to look for the same traits in a futures broker as you do in any other financial services provider.
- They need to be regulated by the FCA, well capitalised and based in a jurisdiction with a proper legal framework.
- As a retail customer or beginner futures trader, you should also expect them to offer segregated accounts for client money and be happy to disclose those details.
- Any broker you trade futures with should also be a member of leading futures exchanges or have agents who are.
Futures Trading Versus CFDs
There are several major differences between futures trading and CFDs:
- Firstly in terms of the counterparty risk when you trade exchange-traded futures your counterparty risk, the risk of not being paid, resides with the clearinghouse, whilst when you trade OTC CFDs or make spread bets your counterparty risk is between you and your provider
- From a structural point of view futures contracts have a finite lifetime and expiry dates, CFDs are typically open-ended and can run indefinitely, though they may become uneconomic to finance over the very long term
- CFDs can also be traded quarterly and structured in a similar way to futures contacts, i.e. with a finite lifespan and financing costs factored into their pricing at the outset, rather than being charged as rollovers/swaps in running
- Profits from both CFD trading and exchange-traded futures are taxable and subject to Capital Gains Tax under UK law.
Futures Trading Versus Spread Betting
The major difference between futures trading and financial spread betting is around tax treatment.
- Profits made from financial spread betting by individual UK taxpayers are currently not subject to Capital Gain Tax (CGT)
- Losses made in futures or CFD trading may be offset against gains made elsewhere, which is not the case for spread-betting losses
- Spread betting is similar to CFDs although unique to the UK, they can vary in duration, they can run on indefinitely like a CFD or they can have daily, weekly or monthly formats and durations.
What Are The Major Exchanges For Futures Trading?
There are many futures trading venues across the globe however the major exchanges are:
- CME (Chicago Mercantile Exchange)
- CBOT (Chicago Board of Trade)
- ICE (Intercontinental Exchange)
- Eurex (European Exchange)
The CME and ICE are US exchanges, they have a global presence and have aggressively grown through acquisitions of smaller rivals over the last decade or more. Eurex is the principal European futures exchange and a genuine competitor to the US businesses. There are also futures exchanges in most major developed and leading developing nations.
Pros Of Futures Trading
The key pros of futures trading are:
✔️Reduced counterparty risk
✔️Financial market transparency
✔️Standardised contracts
✔️Market liquidity
The various benefits from trading futures the central counterparty/clearinghouse model effectively eliminates counterparty risk and guarantees delivery and payment even in the event of default such as the failure of an exchange member.
Futures markets create price discovery across the calendar that benefits both producers and consumers, this is particularly useful in commodity markets, but it also allows us to visualise interest rate and yield curves and future market expectations for a whole host of other markets.
Futures markets offer standardised contracts that trade a fixed quantity and quality of an instrument and these contracts trade in an orderly series or progression to a known expiry and delivery calendar.
Futures contracts can provide instant asset allocation, for example, imagine a fund manager who has a new investment mandate and a view on equities, but who does not yet have their exact stock selection nailed down. The manager can quickly get long or short of equity index futures to gain exposure, then reduce and refine that exposure as when he has a more stock-specific investment list.
Cons Of Futures Trading
The main cons of futures trading are:
❌Volatility
❌Unpredictability
❌Leverage multiples losses
Futures markets can be volatile and are often very sensitive to geopolitical tension, natural disasters and the weather.
The supply of agricultural products and foodstuffs can be greatly affected by climatic events, such as excessive rain or drought, wildfires etc. Whilst oil supplies can be interrupted by conflict, natural disasters or man-made barriers such as sanctions and tariffs.
If supply constraints or fears of one become particularly acute, then futures price can spike very sharply and often without much warning. Conversely, a bumper harvest or expectations of growing supply can quickly depress futures prices.
In a leveraged or margined product, big price swings mean large swings in a traders PnL. If prices move against a trader, then they will need to add variation margin to their account, the clearinghouse may also choose to vary the initial margin required to open and hold positions in volatile futures contracts.
Futures Trading Costs And Fees
The principal costs when trading futures are commissions and exchange fees.
Commissions are typically calculated and charged on what is known as a round trip basis that is the opening and closing of a trade, any exchange fees are usually paid on the opening side of a trade only.
Commissions will vary across products and providers; exchange fees will also vary based on the venue you are trading on. If you are trading in deliverable products, then there may be additional charges associated with delivery and storage. As ever it’s best to be aware of all charges and fees before you trade, and your broker should be happy to provide with that information.
Trading Futures On Margin With Leverage
There are two types of margin you need to consider when trading futures:
- Initial margin
- Variation margin
Margin rates on futures contacts are set by the exchange and clearinghouse, for each contract there will be an initial margin, for example, say US$10,000 per lot or contract traded.
The larger the notional or underlying value of a contract then the larger the initial margin is likely to be.
Variation margin may be required to sustain an open position throughout its lifetime. The more a position moves against you the larger your variation margin liability will be on that position.
Futures exchanges and their clearinghouses use complex mathematical models to determine risk profiles and appropriate margin levels, vanilla long or short positions will have the most straightforward risk profiles, whilst spread trades and other complex strategies will have a very different risk profile.
Variation or maintenance margins are payable on demand if you don’t pay you are likely to be “stopped out”. Active traders will often leave collateral or cash with their broker/the clearinghouse against that possibility.
Most Popular Futures Contracts
Futures volumes have been rising over the last five years as we can see in the graphic below. Global futures volumes reached 54.53 billion in 2022, according to data from the Futures Industry Association.
Equity indices and interest rate futures/options volumes grew by +23% and +24% respectively in 2018 and equity index volumes continued to grow during H1 2019.
Trading volumes reflect global macro themes and changes investor sentiment and it’s interesting to note that both Latin American and Indian futures exchanges saw sharp rises in volumes during 2018.
The Dax 40 the Eurostoxx 50, S&P 500, Nikkei 225 and the FTSE 100 are perennially popular with traders, as are benchmarks such as US ten-year bonds, crude oil and coffee and gold.
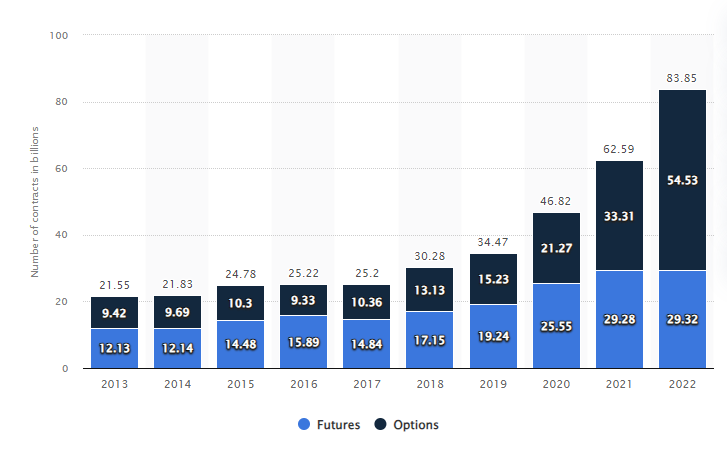
Source: statista.com
Basic Strategy For Futures Trading
The best way to trade futures is to use their underlying characteristics to your advantage.
One of the main benefits of trading futures is the ability to get instant asset allocation. That means that you can trade market sentiment and the changes in it, while it’s happening.
For example, if the market sentiment starts to move towards risk-off perhaps after some poor data or a hawkish central bank statement, traders can quickly get short of risk assets such as equities and long of safe havens such as 10-year bonds and gold as and when the market mood swings back towards risk-on traders will look to take the opposite positions i.e. long risk assets short safe-havens.
Futures are often driven by market momentum and from our experience, they tend to respect support and resistance levels, so knowing where recent period highs, lows and key moving averages are on the chart can be a powerful tool. Trading the price action at those levels (breakouts, failures etc.) can be an effective way to trade futures.
Of course, traders will always need to be on the lookout for false breakouts when pursuing this type of strategy good money management and stop-loss placement will also play a big part.
Futures Trading FAQs:
Futures Broker FAQs:
Futures brokers mainly make money through commissions. But they also have a few additional revenue streams including:
- Commission- this is charged on a per-lot basis for every lot traded.
- Exchange fees- this is a fee charged by the exchange that the broker either includes in the commission or passes on to the client.
- Foreign exchange- futures are settled in various different currencies, so if you are trading USD-denominated futures and your account is in GBP, there will be a cost to convert USD P&L into GBP.
- Account interest- if you are running an account overdraft in either your base currency or other currencies, your account will be charged interest every day that it is overdrawn.
Futures brokers are often referred to as futures and options brokers, as futures brokers also provide access to the options markets. Options contracts are traded on the same exchanges as futures options. For example, a futures broker will provide access to FTSE futures as well as FTSE options. It is possible to trade futures and options strategies that offset the exposure of futures and options. For example, buying call options and selling FTSE futures to speculate on, or protect against volatility. For more information on options brokers, please refer to our guide on options trading or compare options brokers here.
A discount futures broker offers clients significantly reduced fees for online trading and algorithmic trading. For futures traders that trade in significant volume, futures brokers will reduce commission and the exchanges will also reduce exchange fees. Futures brokers are able to negotiate these discounts on behalf of their clients, based on the volume of trades that are placed.
Yes, if you want to keep a futures position past expiry, you roll the position into the next month by closing and opening existing and new positions simultaneously. You can either do this online, or if you can’t figure out which way the spread works, give them a call and ask them to do it for you. That way, if they get it wrong too, they have to cover the loss.

Richard Berry
This article contains affiliate links which may earn us some form of income if you go on to open an account. However, if you would rather visit the futures brokers via a non-affiliate link, you can view their futures trading pages directly here:
