-
 Richard Berry
Richard Berry
- Updated
Index brokers provide access to indices markets such as the FTSE, DAX, and S&P for the purposes of trading, speculation, and hedging. These indices are made up of individual shares traded on stock exchanges. For example, the FTSE 100 is an index of the 100 biggest publicly listed shares traded on the London Stock Exchange.
| Name | Logo | Index Markets | FTSE Spreads | GMG Rating | Customer Reviews | CTA | Feature | Expand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Index Markets 40 |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 3.8
(Based on 124 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 69% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
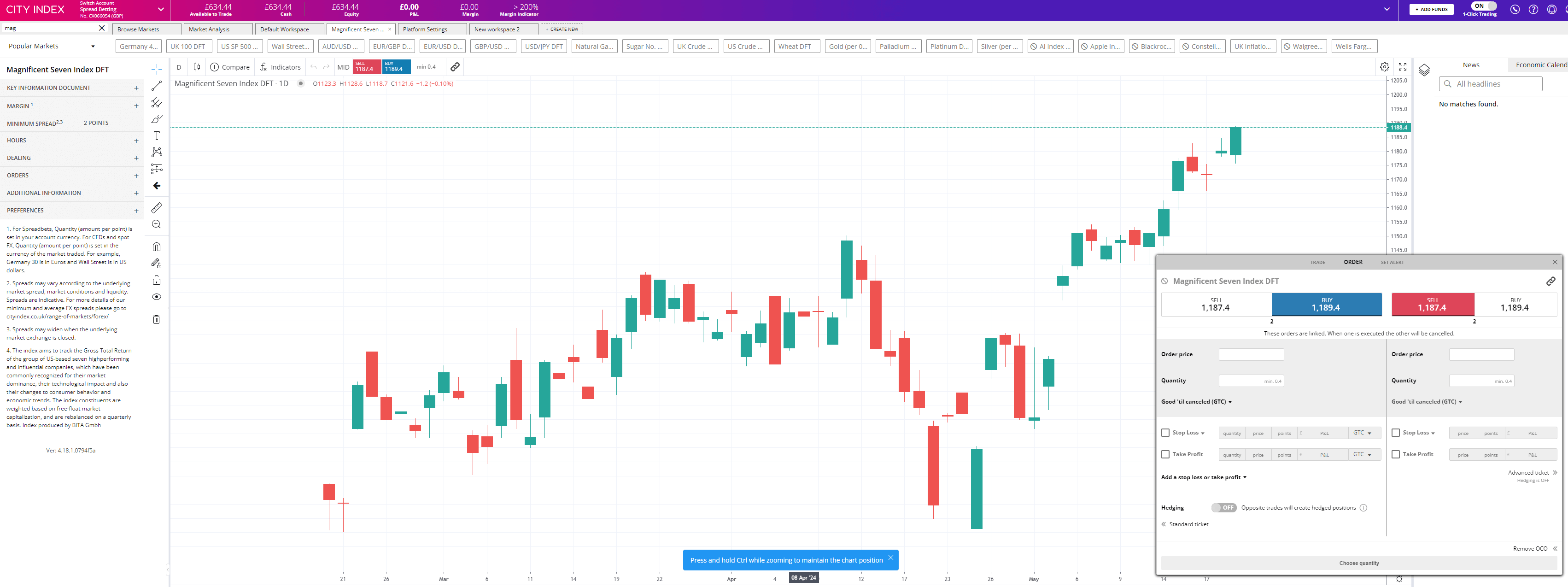
City Index recently boosted tradable indices with a Magnificent Seven basket Provider: City Index Indices Trading Verdict: Trade major global indices at City Index like the UK 100, Wall Street and Germany 40. Choose a spread betting or CFD trading account and get tight spreads on European, US, Asian and Australian indices. City Index also provide trading signals through and post trade analytics to provide trading ideas and improve your performance. Is City Index good for indices trading? Yes, you can trade around 40 indices with City Index, which is more than the majority of trading platforms. As the name suggests, City Index started out as an indices broker, as remarkably indices have always been more popular than forex trading with UK traders. City Index are towards the top of the range when it comes to indices on offer, mid-range when it comes to index spreads and one of the best brokers for index trading signals (as they provide their own rather than buying them in from a firm like Acuity Trading).
Index baskets City Index, has recently launched a new index basket based on the Magnificent Seven stocks. The basket, which contains a “who’s who” of US tech and growth stocks, will allow City Index’s clients to get instant exposure to this influential grouping, in a single trade. This means that you can take long or short positions on the Mag 7 stocks in one trade with equal ease. Named after the protagonists in the classic Western of the same name, the Magnificent Seven are seven US based Technology, Communication Services and Consumer Discretionary stocks which have dominated global equity markets since the pandemic. The Mag 7 group comprises Alphabet, Apple, Amazon, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, Nvidia and Tesla. These are all household names and account for around 30% of the market cap of the S&P 500 index, which represents some 80% of the total US market cap, and as much as 60% of the total global market cap. Looking back at the historic performance of the Magnificent Seven we find that they have had an annualised return of almost 31.0% over the last five years. City’s Magnificent Seven index benchmarks the BITA US Magnificent Seven index. BITA is a German fintech and index solutions provider. Their Magnificent Seven index is a free-float market cap-weighted benchmark with quarterly rebalances. The City Index Magnificent Seven basket is traded as an index product during the regular session of the US market, which is open between 14.30 and 21.00 London time.
The product can be traded as a CFD or a spread bet utilising any of City Index’s trading platforms, whether desktop or mobile. The index will have a 6.0 point spread and margin rate of 10.0% It could be argued that the influence of the Magnificent Seven has waned recently. However, they are some of the largest companies in the world and they are intimately connected to globally important themes, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence and the energy transition. Being able to trade these stocks in a single deal should be very advantageous for City Index clients, as price movements in the group reflect changes in trading sentiment and Risk-on/Risk-off behaviour in the equity market.
Pros
Cons
Overall4.1 |
||
|
Index Markets 40 |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.2
(Based on 19 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 74% of retail CFD accounts lose money. |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index pricing: FTSE 1, DAX 1, Dow 3.5, NASDAQ 1, S&P 0.4. |
||
|
Index Markets 50+ |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.8
(Based on 1,812 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 62% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Capital.com Voted Best Trading Account In 2025 Provider: Capital.com Verdict: Capital.com won the People’s Choice vote for “Best Trading Account” in the 2025 Good Money Guide Awards and “Best Trading App” in our 2023 awards as they have one of the most intuitive apps for trading the most popular markets globally. Capital.com was founded in 2016 and is a CFD trading platform broker with offices in the UK and around the world. Since then, they have grown to offer over 3,000 tradable assets to 100,000 monthly active clients. Is Capital.com any good for trading? Capital.com has a user friendly and intuitive trading platform and app, that gives access to the most popular financial markets with competitive spreads with the ability to reduce risk by decreasing your leverage. Trading via the app has always been capital.com’s forte, and in 202, it won our award for “best trading app” not in part due to the fact that the company CTO has extensive experience in building engaging apps like Candy Crush. What makes Capital.com different? Thumbs up, literally Do you know what one of the most impressive thing about Capital.com is? They put the buy and sell buttons at the bottom of the app. I don’t mean that in a facetious way, it’s genuinely a brilliant feature. This may not sound like much but it’s a good example of how Capital.com has integrated decades of analytics, experience, feedback and customer data into creating a very easy-to-use intuitive trading app from scratch. When Capital.com first became authorised by the FCA back in 2018, I visited their offices in London to have a chat about what they offer. The two main things we discussed were button placement and AI. Trading App But anyway, if you’ve updated your iPhone to the latest iOS you’ll notice that Apple has started moving things to the bottom of the screen, the search bar for instance. This is because, phones are getting bigger, and your thumb can’t reach the top of the screen if you are holding it with one hand. This is something that Capital.com figured out would make trading easier 5 years ago. I’ve just been through a bunch of other trading apps on my phone and still, amazingly enough, none of the other brokers have done this yet.
Capital.com was also the first to integrate artificial intelligence to help you improve your trading, they say, based on the Martingale theory. When I spoke to Chris Demetriou, the head of sales in the UK, he said that the system should give you prompts based on your previous trades. So for example, if you are about to do a trade that is similar to ones you have constantly lost on before, you should get a “are you sure you want to do this” notification. Leverage Control Everybody knows, that one of the main reasons people lose money when trading is overleverage. This could be either from not having enough free cash on account to give your position breathing space, or simply putting on trades that are too risky. One really good feature is that you can change your leverage based on asset class. The default leverage is the max that retail traders in the UK are permitted, but you can change this to 1:1 so you need to fully pay up for positions. A sensible thing to do if you are just getting started, which can help reduce excessive losses. As your experience grows you can increase your leverage accordingly. Hedging You can also set the platform to put on hedging positions, so you can be long and short the same thing at the same time. Why you ask? Well, it can help you run longer-term positions and short-term hedges. This in fact is the very point of CFDs. They were originally hedging tools, and still a good way to protect your long-term investment portfolio against short-term market corrections without having to close off your positions. Customer Support Customer support is pretty good too, you can get in touch via the chat widget on the platform, whatsapp or telegram. When I tested it I got a response within a minute and the issue I had was dealt with quickly (uploading ID to verify my account if you must know). TradingView You can’t trade from the charts, but when you have open positions they are overlayed along with your stops and limits, which you can move by dragging and dropping. But, if charting is your thing, you can join the other 78,000 Capital.com customers using and trading from TradingView. Proprietory Tech One thing I quite like though is that instead of relying on third-party software, the Capital.com trading platform is built in-house, and if you want something you can ask for it. For example, previously on the app you could see where an asset is as a percentage relative to the daily range. But, a customer asked, if you could see it in points too. So, that was quickly integrated so that you can now toggle between percentages and points. A small thing, but indicative of a broker that can do things and does do things, rather than just logging a helpdesk ticket. Refinitiv There are no trading signals on the platform or app, but you do get access to Refinitiv reports on US stocks, which give you a good overview of historic and potential future financial health. A good feature for those looking at slightly longer-term positions. Overnight funding Talking of long positions, or longer long positions, Capital.com also display quite clearly what your overnight financing rates are going to be on a daily basis. I’m sure this is a regulatory obligation anyway, but it’s done in a way that you can actually see what the price is, rather than an opaque formula. It gives a bit more transparency about how much a position is going to cost you. Investmate If you are new to trading, they have a stand-alone app called Investmate, which puts you through a series of bitesize courses that explain the financial markets. Capital.com also own currency.com if you fancy a punt on crypto, and shares.com so we can expect to see more comprehensive physical investing options soon. Pros
Cons
Overall4.5 |
||
|
Index Markets 39 |
FTSE Spreads 2 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 3.7
(Based on 146 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 76% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Plus500 Expert Review 2026: A user-friendly platform with access to global markets Provider: Plus500 Verdict: Plus500 is one of the largest online trading platforms and operates in more than 50 countries worldwide. Founded in 2008, it has more than 26 million customers today.
Plus500 is headquartered in Israel, however, it’s listed in the UK on the London Stock Exchange (it’s a member of the FTSE 250 index). Here in Britain, its platform is operated by Plus500UK Ltd, which has offices in London.
In the UK, you can only trade CFDs with Plus500. CFDs are financial instruments that allow you to profit from the price movements of a security without owning the underlying security itself. 76% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. Is Plus500 a good broker? Yes, Plus500’s trading platform has evolved nicely over the years from a simple interface to an intuitive execution venue for CFDs on the major markets and stocks. Opening a Plus500 account is really simple:
Pricing: It’s dynamic so moves with the market for minimum spreads. Plus500 does not charge any trading commissions when you place a CFD trade. However, there are some fees you need to be aware of including:
Withdrawals are free of charge no matter how many you make per month. Deposits are also free of charge. Market Access: Very good, Plus500 are always first to try new asset classes With Plus500, you can trade CFDs on a range of assets and instruments including:
Overall, there are over 2,800 assets you can trade with CFDs. The maximum amount of leverage you can use with Plus500 varies depending on the asset class as shown in the table below. If you are trading forex, you can potentially borrow up to 30 times your own money. For shares, you can only borrow up to five times your own capital. Plus500 margin rates:
Platform & Apps: Basic execution, but it does the job well Plus500 trading apps and platform also offers several tools to help traders manage risk including:
Customer Service: Plus500 doesn’t have a phone option, but its live chat is sufficient Plus500’s customer service options are limited to online chat, email and WhatsApp. So, you can’t contact the company by telephone. However, don’t let that put you off. We contacted the company via online chat and were very impressed with the service and support offered. It’s worth noting that support is available 24/7. This is a big plus – some other CFD providers only provide support during the week. If you are a larger or professional trader you can get access to Plus500’s Premium Service Package which includes:
The premium service is invitation only. To become a premium customer, you must have a real-money trading account. However, if you want better margin rates but are not interested in the premium package you can upgrade to a professional account. The Plus500 professional account is an account designed for professional traders. With this account, you have access to higher levels of leverage (e.g. 1:20 for shares). To be eligible for a professional account, you must meet two of the following three criteria:
Research & Analysis: Some sentiment, but limited education and analysis. Plus500 offers a range of additional features designed to help traders make money, including:
Pros
Cons
Overall4.6 |
||
|
Index Markets 28 |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.6
(Based on 86 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 71.9% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index pricing: FTSE 1, DAX 1, Dow 2, NASDAQ 1, S&P 0.4.Pepperstone sources razor-sharp pricing, from multiple Tier 1 banks and liquidity providers, with competitive fixed spreads as low as 1 point on UK100, 0.9 on GER40, with no commissions. 99.99% fill rate*, fast execution and no dealing desk intervention. Quick and easy account opening. Apply for your trading account in few minutes. |
||
|
Index Markets 30 |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.3
(Based on 257 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 61% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index pricing: FTSE 1, DAX 1, Dow 4, NASDAQ 2, S&P 0.6.
Spreadex offers 24 hour indices trading via financial spread betting or Contracts For Difference on the world’s major stock indices – with spreads on the most popular markets from 1pt on UK 100, 1pt on Germany 40 & 1.7pts on Wall Street.
|
||
|
Index Markets 80+ |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 3.9
(Based on 695 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 68% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index pricing: FTSE 1, DAX 1, Dow 2.4, NASDAQ 1, S&P 0.4.
Trade over 80 indices with the world’s No.1 spread betting and CFD provider. Trade with deep liquidity on spreads from 1 point on the FTSE 100, 1.2 on the Germany 40 and 0.4 on the US 500. IG also offers indices trading on weekends when the main markets are closed. |
||
|
Index Markets 80+ |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 3.7
(Based on 149 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 68% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index pricing: FTSE 1, DAX 1, Dow 2, NASDAQ 1, S&P 0.5.
CMC Markets lets you trade on over 80 cash and forward global indices based on the FTSE 100 and more, with leverage, on an award-winning spread betting and CFD platform. Trade indices with tight spreads, lightning-fast execution and the highest-rated customer service in the industry. |
||
|
Index Markets 25 |
FTSE Spreads 1.7 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.6
(Based on 136 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 72% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index Pricing: FTSE 1.7, DAX 1, Dow 3, NASDAQ 1, S&P 0.5.
One of the good things about index trading with XTB, is that you can see market depth on the sidebar when trading indices. I’ve included that as a screenshot in the index trading platform tab below.
This may not be such an issue if you are a smaller trader, but if you are dealing in size then people able to see what volume you will get filled in is very handy.
You can also deal direct from the charts, so if you use the crosshairs function, you can quickly place orders around key support and resistance levels. |
||
|
Index Markets 29 |
FTSE Spreads 1 |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.1
(Based on 125 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 62% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Index pricing: FTSE 1, DAX 1, Dow 3, NASDAQ 1, S&P 0.5.
Is Saxo good for indices trading?
Yes, with Saxo you can trade 29 index-tracking CFDs with fast and reliable access to the markets from your phone, tablet, laptop or multi-screen desktop setup. The award-winning, multi-device SaxoTraderGO partners seamlessly with SaxoTraderPRO, giving a professional-grade platform for advanced index traders. |
||
|
Index Markets 13 |
FTSE Spreads 0.005% |
GMG Rating |
Customer Reviews 4.5
(Based on 1,347 reviews)
|
Visit Platform 59.7% of retail investor accounts lose money |
Index Trading Account Types:
|
Interactive Brokers (IBKR) Offer Indices Trading On Global Markets Account: Interactive Brokers (IBKR) Index Trading Description: You can trade the global stock market and synthetic on-exchange indices as either a futures contract, DMA option of equity as an ETF. Interactive Brokers has transparent, low commissions and financing rates. Equity indices can be traded in lots as small as 1x the index level. Unlike the related futures, Index CFDs (not available in the US) do not expire, saving rollover-related costs and risks. Is IBKR good for indices trading? Yes, IBKR is an excellent choice for index trading. For beginners, Interactive Brokers offers a wide range of ETFs that track underlying stock market indices like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones. For more advanced traders, IBKR offers DMA index futures trading with low commissions. Pricing: IBKR is always a cheap way to trade, one of the original discount execution only brokers. Market Access: A huge range of on-exchange ETFs or direct market access to index futures around the world. App & Platform: Excellent – something for everyone from beginners to hedge funds. Customer Service: A bit hit and miss sometimes, but their AI bot can solve most issues and personal dealers for larger accounts. Research & Analysis: A constantly updating stream of analysis and data on global indices. Pros
Cons
Overall4.9 |
Methodology: The Good Money Guide team chose what we think are the best brokers for indices based on:
- Over 30,000 consumer votes and reviews in the annual Good Money Guide awards
- Our experts’ own experiences testing the index trading platforms with real money
- In-depth comparison of the features that make them stand out compared to alternatives
- Good Money Guide’s exclusive interviews with the index broker CEOs and senior management
Best Platform For Beginner Index Traders
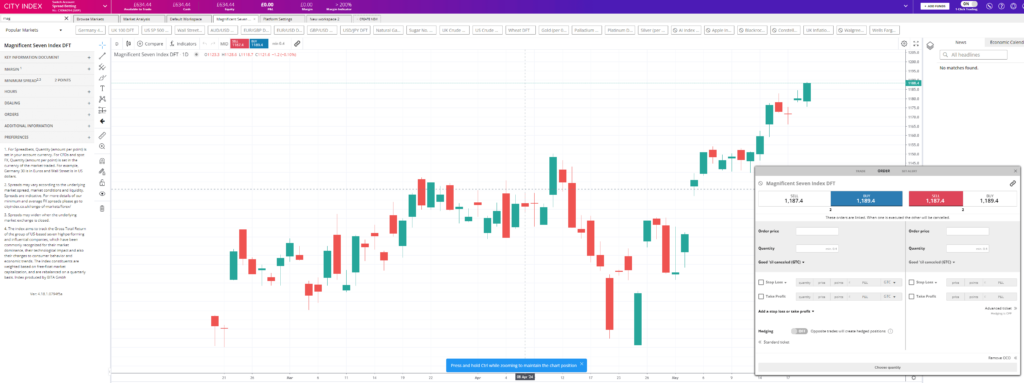
City Index is an excellent broker for beginners as they have a simple trading platform with 40 major indices to trade as CFDs and spread bets.
They also provide plenty of educational material, and have trading signals on indices which show potentially good times to buy and sell through two signal providers.
This table of index brokers shows which indices trading platforms offer features that can benefit new traders.
| Beginner Features: | Trading Signals | Educational Webinars | Client Sentiment | Leverage Control | Low-Risk Products | Investment Account |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Index | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Interactive Brokers | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Plus500 | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| CMC Markets | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Pepperstone | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Spreadex | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Saxo | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| IG | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| XTB | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| eToro | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Best Index Trading For Advanced & Professional Traders
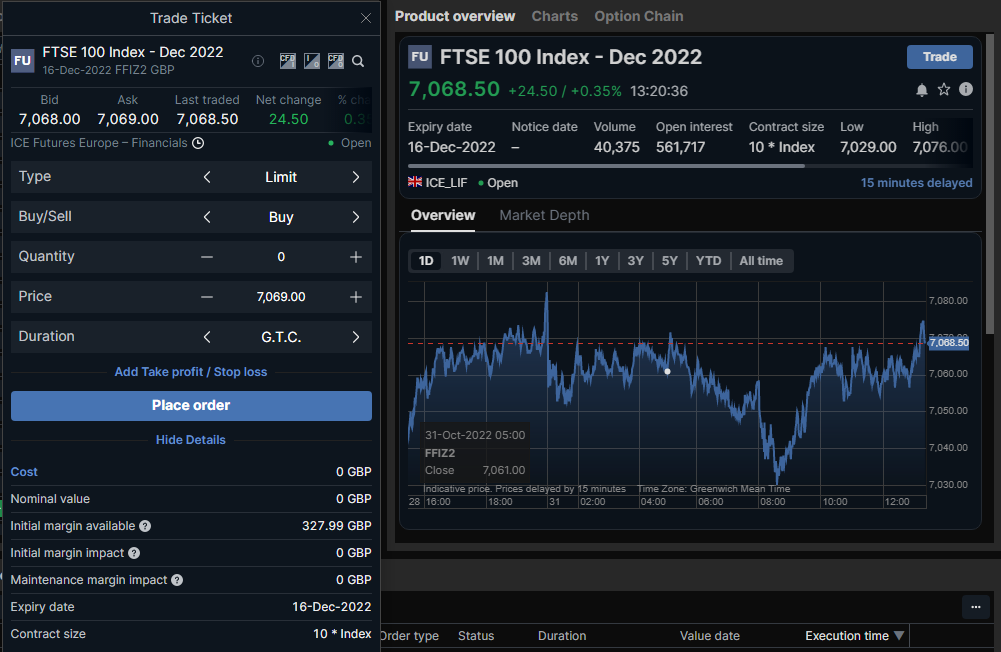
Saxo is the best broker for sophisticated and high-net-worth index traders as their platform is geared towards professional traders placing large orders.
Saxo also have some complex order functionality and direct markets access to global exchanges through futures and options.
This comparison table shows what index brokers offer functionality for advanced index traders.
| Advanced Features: | Voice Brokerage | Corporate Accounts | Level-2 & DMA | Algo/API Trading | Prime Brokerage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Index | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Interactive Brokers | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Plus500 | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| CMC Markets | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Pepperstone | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Spreadex | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Saxo | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| IG | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| XTB | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Best For Market Access

IG and CMC Markets both offer over 80 indices for trading as a spread bet or CFD.
This table shows which brokers offer access to the most indices as well as peripheral markets.
| Market Access: | Total Markets | Forex Pairs | Commodities | Indices | UK Stocks | US Stocks | ETFs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Index | 13,500 | 84 | 25 | 21 | 3500 | 1000 | n/a |
| IG | 15,000 | 80 | 38 | 34 | 3925 | 6352 | 2000 |
| CMC Markets | 12,000 | 338 | 124 | 82 | 745 | 4968 | 1084 |
| Pepperstone | 1,350 | 90 | 32 | 28 | 192 | 880 | 107 |
| Saxo | 8,600 | 182 | 19 | 29 | 5000 | 2000 | 675 |
| Interactive Brokers | 8,500 | 100 | 20 | 13 | 500 | 3500 | 1100 |
| Spreadex | 10,000 | 60 | 20 | 17 | 1575 | 2110 | 160 |
| XTB | 2,000 | 60 | 22 | 25 | 230 | 1080 | 138 |
Best Index Trading For Commissions & Fees

CMC Markets is one of the cheapest brokers for indices, with some of the tightest spreads for CFDs and spread betting on the major exchanges.
As well as our index cost comparison, you can use our trading fee calculator to see how much it will cost you to trade over a year with various different brokers.
| Trading Costs | FTSE 100 | DAX 30 | DJIA | NASDAQ | S&P 500 | EURUSD | GBPUSD | USDJPY | Gold | Crude Oil | UK Stocks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Index | 1 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.008 |
| IG | 1 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.28 | 0.001 |
| CMC Markets | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 3 | 0.001 |
| Pepperstone | 1 | 0.9 | 2.4 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.001 |
| Saxo | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0005 |
| Interactive Brokers | 0.01% | 0.01% | 0.01% | 0.01% | 0.01% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.02% |
| Spreadex | 1 | 1.2 | 4 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.002 |
| XTB | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.0008 |
Best For Account Types
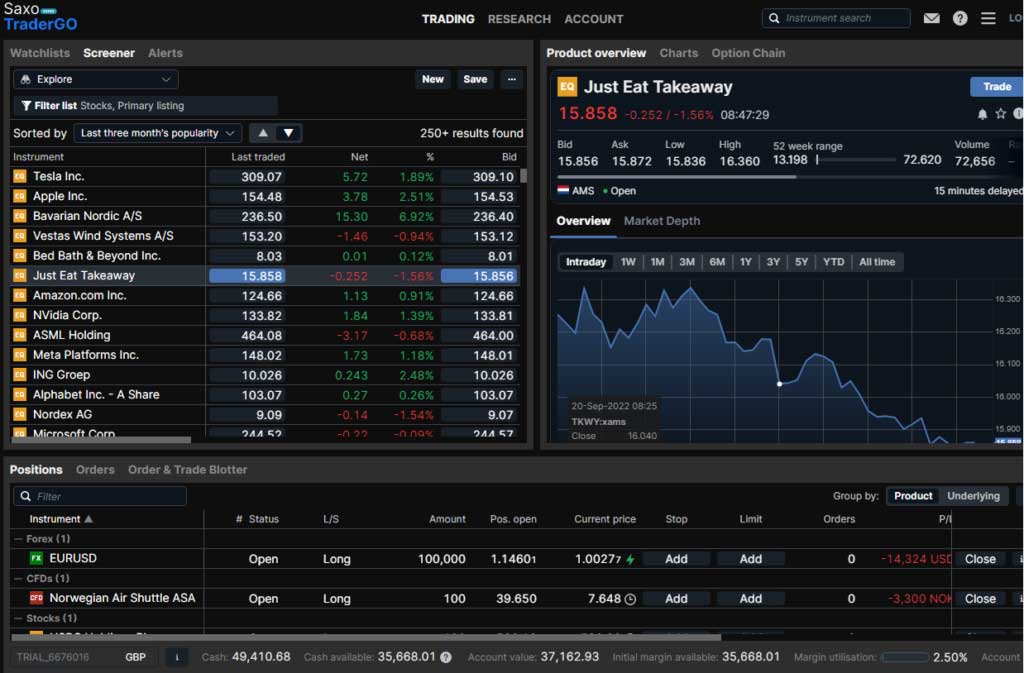
Saxo provides the most ways to trade indices as they offer index CFDs as well as on exchange-traded futures, options and ETFs. The only type of index trading Saxo Markets does not offer is spread betting.
If you would like to trade indices as a spread bet, IG also offer spread betting, CFDs and physical ETFs, although not DMA futures and options.
Use our comparison table of what we think are the best index trading platforms to compare how many indices they offer, commission and spreads on the most popular indices and what different types of accounts they offer.
| Account Types: | CFD Trading | Spread Betting | DMA | Pro Accounts | Investments | Futures & Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Index | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Interactive Brokers | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| CMC Markets | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Pepperstone | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Spreadex | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Saxo | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| IG | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ |
| XTB | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ |
Index brokers provide access to stock market indices markets via:
- Index Futures– these index brokers provide professional traders with direct market access to indices traded on exchange.
- Index Options– these offer options trading to professional traders on-exchange. In some cases, stock brokers will offer index options for clients that want to hedge a portfolio.
- Index CFDs – these provide CFDs (contracts for difference) which are ideal for traders that want to trade in smaller size than index futures.
- Index Spread Betting – these index brokers let their clients bet on the price movements of an index. As trades are structured as bets, there is no capital gains tax due on index spread betting profits
- Index ETFs – index ETFs are listed on stock exchanges and can be bought and sold in a similar way to shares and can track the price of an index. They are useful for investors that want exposure to an indices’ overall performance but do not want to buy an actively managed index fund or index derivatives. As they are listed on stock exchanges, they are available through share dealing platforms, CFD trading platforms and spread betting brokers.
✔️ FCA Regulation & Your Peace Of Mind
Good Money Guide only features index trading platforms that are regulated by the FCA, where your funds are protected by the FSCS (Financial Services Compensation Scheme).
All index trading platforms that operate in the UK must be regulated by the FCA. The FCA is the Financial Conduct Authority and is responsible for ensuring that UK index trading platforms are properly capitalised, treat customers fairly and have sufficient compliance systems in place.
How To Trade Indices – Index Trading Explained
To trade indices you need an index broker like IG, Saxo Markets or Interactive Brokers that can give you access to indices through OTC products like CFDs or on exchange future and options. Index trading is speculating on stock market indices like the FTSE 100, S&P 500, DAX, IBEX and the CAC. Indices trading is one of the most popular types of day trading around the world. In this guide we explain how to trade indices and what to watch out for.
5 Easy Steps To Trade Indices
- Open an account with an indices trading platform (IG is good for spread betting, CMC Markets for CFDs and Saxo Markets for futures and options).
- Choose how you want to trade indices (spread betting is tax-free profits, and futures and options give you direct market access.
- Deposit funds into your brokerage account
- Select your indices by searching for their code (FTSE 100 is UKX, S&P500 is US500 and so on)
- Execute a trade and speculate on if it will go up or down and buy (go long) or sell (go short).
Different Ways To Trade Indices
If you want to speculate on indices (with leverage), here are the three most popular ways:
1) Futures Contracts
Futures index derivative contracts are popular among traders. These contracts are flexible to incorporate many features including leverage and minimal tracking error. You can trade with direct market access on exchanges like ICE, NYSE, NASDAQ and CBOE. A few indices have ‘mini futures’ (such as mini Dax or mini S&P 500) to cater for traders with a small account. Bear in mind futures (trading through futures brokers) are a professional trading product and only available to clients that have sufficient experience and funds. For traders that do not qualify for a professional trading account liquidity issues are basically moot as traders that do not qualify as professional should not really be trading in the volumes and size that would require additional margin.
2) Spread Betting
Place bets on a £ per point basis as to whether you think the price will move up or down. There is no capital gains tax on profits as trades are structured as bets. The costs to spread betting are the spreads to open and close positions. Most brokers offer competitive pricing on equity indices. For example here with IG, spreads on the FTSE are 1 point, 2.4 on the Dow and 0.6 on the S&P.
3) CFDs (Contracts for Difference)
You speculate on the opening and closing price of your chosen equity index. This is a form of leveraged trading. CFDs are popular for index trading outside of the UK where financial spread betting is not available.
Industry experts told us
"Index trading provides an excellent way to speculate or hedge on the overall performance of the largest listed companies within a regional economy like the FTSE for the UK or the S&P500 in the US. Another particularly useful aspect is being able to trade one indices' performance against another which can protect you from dramatic overall market moves."Cost Of Trading Indices
There are two types of spreads on index trading – fixed and variable.
Fixed means that the difference between the buy and sell price will always be the same. For example, the spreads on Wall Street at always 1 point, the DAX is 1 point and the S&P is 3 points.
Variable spreads mean that the difference between the buy and sell price will change depending on how liquid and volatile the market is. For example, around non-farm payrolls, the market will be more volatile and the best bid offer prices will not have as much liquidity. Therefore, the prices will be slightly further apart.
- Related guide: 50 rules for successful trading
For example here with IG, spreads on the FTSE are 1 point, 2.4 on the Dow and 0.6 on the S&P.
It’s a bit ‘swings and roundabouts’ really. You know where you are with fixed spreads, but with variable spreads, during normal market trading you can get tighter prices, but they widen as the underlying market widens.
Spread betting and CFD trading on the major indices is risky.
Leveraged Index Trading
A quick note about the above trading methods. These vehicles can be risky because they have embedded leverage. This means that you can lose capital far more than anticipated on a ‘bad’ day – a session where prices move sharply against your positions. In other words, the trading account has to have sufficient capital buffer to withstand these fluctuations.
The second point concerns the spread between the buy and sell prices. When a market becomes extremely volatile, spreads will increase (sometimes dramatically) as brokers, market makers and large investors all want to dump large positions simultaneously. Prices may leap or plunge in seconds.
For example, around US non-farm payrolls, the market will be more volatile and the best bid offer prices will not have as much liquidity. Therefore, the prices will be further apart.
Volatile pricing may hit the stops (always have them when opening positions) and then prices bounce back near the starting points.
Lastly, if at any point you find that these leverage trading is not working and is depleting your capital at a high rate, switch to investing as leverage is much lower. There are many equity-based ETFs that you can buy and hold in your portfolio. This provides an equivalent exposure (since both instruments are based on the same underlying equity index) but with easier-to-manage portfolio risk.
Second only to forex trading, indices offer good liquidity, a decent intra-day range and pretty much 24 hour news flow.
SPDR iShares 500 (SPY), for example, is the largest ETF in the world that tracks the S&P 500 index. You can buy this ETF for your stock portfolio.
Why Are Indices So Popular In Trading?
Major indices are also some of the most liquid tradable assets out there so no matter how big a trader you are your orders should always get filled.
As index trading is heavily influenced by a combination of the individual constituents of an index, overall economic data and self-fulfilling technical analysis there is a never ending supply of news, events and signals to trade from.
Traders analyse and develop judgements on major stock market indices like the FTSE 100, S&P 500, DAX, or the Nikkei 225. Then, active bets are placed on the direction of the index. But who trades equity indices? Institutional portfolio managers, traders and investors all trade equity indices in major financial markets. Liquidity is excellent; exposure easily adjustable. Leverage is attainable via futures. Their trading time frames may range from intraday to multi-month. In sum, index trading is no more sophisticated than Forex trading as long as you understand the basics and master the rhythm of the market.
The rest of this guide helps you to understand these indices, what they are and how to trade them.
How Does Trading An Index Work?
An equity index is basically an artificial financial construct whose value is derived from a fixed number of stock prices. Of course, the larger the index, the more constituents it has. Investors often use these indices to describe, measure and compare the aggregate performances of a group of selected stocks.
For example, there is a stock index for the large-cap (called blue chips); and another for the mid-cap. Often, there is another for the small-cap stocks – stocks whose market capitalisations are among the smallest in a market.
A stock index, unlike a stock security, can’t be traded directly. Instead, you have to purchase a security or derivative that is based on the index, such as an ETF or index fund or futures.
Another point worth noting is that a stock index’s minute-to-minute value fluctuation relies on individual stock prices. Depending on the calculation method, a stock with a higher market capitalisation often influences the index more than a small one.
What makes equity indices popular is due to decent intra-day ranges and pretty much 24 hour news flow. The constant release of economic figures and leading indicators creates sufficient price volatility to trade in most sessions.
Major equity indices are also some of the most liquid tradable assets out there, so no matter how big a trader you are your orders should always get filled.
One of the well-known equity indices is the US S&P 500 Index, arguably the most important equity index in the world. The index encompasses many global stocks such as Apple (AAPL), Microsoft (MSFT) and Exxon (XOM).
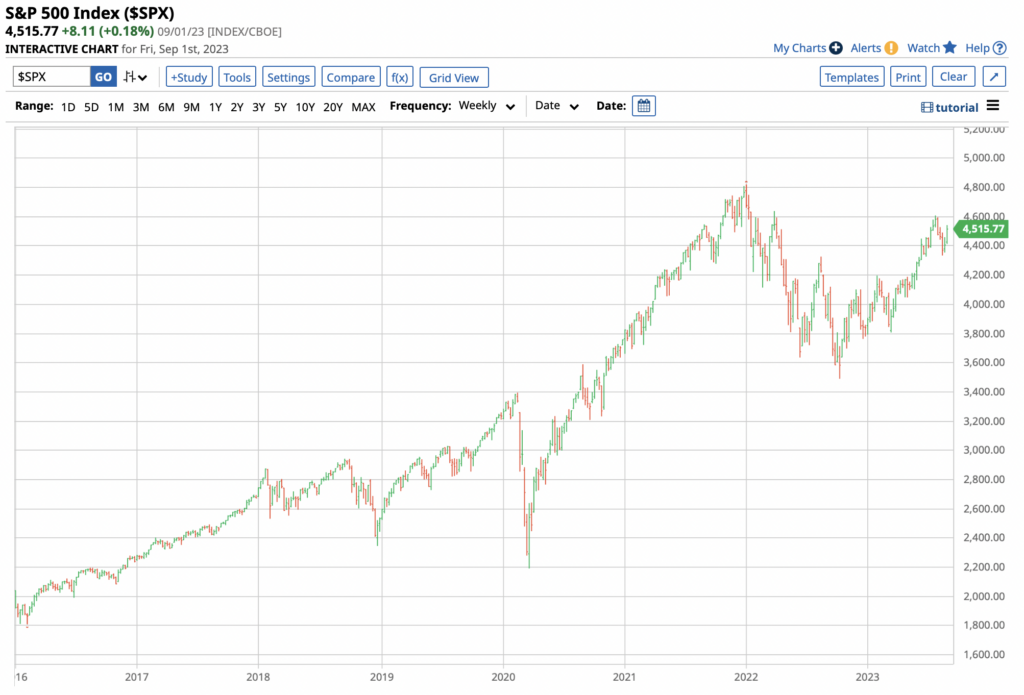
Source: Barchart.com
Benefits Of Trading Equity Indices
Equity indices are popular trading vehicles. There are a few reasons their popularity:
- Equity indices are linked to macro cycles – Since stock markets are proxies for the underlying economy. While it is true that the economy and stock market may not move together all the time, they do synchronise. During a recession, companies report losses and lower profits. This dents stock prices. Ergo, stock indices are popular instruments to trade the macro outlook.
- Equity indices provide diversification. Investors can trade equity indices across different countries. And because the underlying economies grow differently, this means their stock markets zig-zag at a different pace. This provides some diversification to a portfolio.
- Equity indices do not go bust. Unlike stocks. By and large, an equity index is made up of stronger stocks. Weaker companies are gradually deleted from the constituents list – known as ‘rebalancing’ – to maintain the vitality of the index. Yes an index may drop by two-thirds, but it will not fall to zero.
- Key equity indices are liquid. Investment and derivative instruments that based on major equity indices generally have good liquidity and easy to trade.
- Equity indices are used to hedge underlying stock exposure. Given the good liquidity portfolio managers used equity indices to hedge (albeit imperfectly) their equity exposure. Trading in most blue-chip indices are active.
Most Popular Types Of Indices Trading
We’ve covered the best indices to trade in a separate guide, but here we will run through the most popular regions for index trading.
US Indices
The US stock market is the largest in the world. The depth of the American capital market is unrivalled due to presence of Wall Street and numerous global-leading major technology companies (eg Apple or Tesla). Trading activities in Wall Street are hectic; liquidity is excellent. Three favourite US equity indices to trade are: S&P 500, Nasdaq and Dow.
European Equity Indices
Next on our list of the most popular equity Indies to trade are based in Europe. The continent is home to numerous industrial powerhouses and fashion businesses, many of which are world class, eg LVMH, BMW, and BASF. Because of this, Europe is one of the best places to invest and trade. Since not all European financial markets offer similar depth of liquidity, traders look to larger ones, such as DAX and CAC.
Asia Equity Indices
Asia includes a huge swath of the world’s population. Many Asian countries are still developing. This means that the continent houses a large number of fast-growing companies. This excites many investors since returns are potentially massive. As an example, look no further than VinFast – a 6-year old Vietnamese EV maker that, after its 2023 IPO, was briefly worth 3x Volkswagen’s market cap.
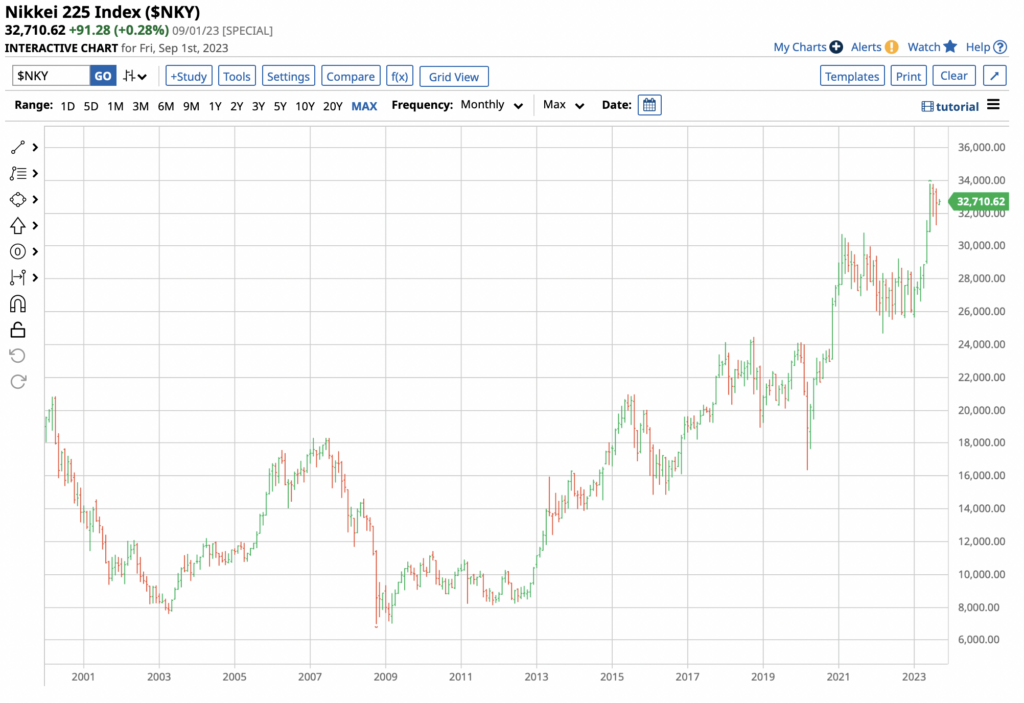
Apart from Japan and HK, there are a few Asian indices that foreign investors preferred to trade, including India’s Sensex Index, Singapore’s Straits Times Index Index, Korea’s KOSPI Index, and the Australia’s S&P/ASX200 Index. Many of these indices are heavily skewed toward certain sectors. For example, the Aussie index contains plenty of mining and natural resource stocks due to the richness of natural minerals in the country.
What Moves Index Prices?
Knowing these indices is only the first step towards profitable trading. Calculations aside, the most important things to know about these stock indices are:
- Index Methodology and Constituents Makeup. How are the indices calculated? Some are market-weighted; some are price-weighted (eg Dow). Within the constituent list, what companies are the largest? One general rule of thumb is this: The bigger the company, the more influence it will have on the index. This influence is especially large if the index has less than 50 components.
- Sector Representation. Some indices are heavily skewed towards certain sectors. This means that the rise and fall of that particular industry may result in the movement of the aggregate index.
- Index Historical Movements. Find out what had happened in the past. In Japan, for example, earthquakes (’95) and tsunamis can have large – but temporarily – impact on the stock market. In the US, prices can collapse 20% in a day (’87) or plunged 9% intraday (2010). When an equity index suffered from a collapse of an asset bubble, chances are prices will drop further.
- Macro Factors – such as tariffs, interest rates, unemployment, inflation can all impact the stock markets one way or another.
- Technical Trends – occasionally an index can be influenced by technical trends. For instance, when an index surged past 3,000 to record highs may lead to more momentum buying thus creating further demand. Major round number levels can sometimes act as support or resistance to a trend. A quick glance at Nasdaq Composite below shows major support at 10,000.
Where Can You Trade Indices?
Aside from market makers that are required to create some minimum liquidity, there are no set rules for OTC brokers to provide liquidity. Liquidity is based on the underlying market as some brokers will need to hedge client index positions. If the underlying market has thin liquidity, so will your broker.
However, some brokers also limit liquidity based on position size or overall exposure. Retail trading accounts will get less OTC liquidity that professional trading accounts. Also, there will be position limits based on overall exposure. If a trading account only has one position it will be heavily exposed to that market, but if there is a diverse portfolio of positions, position limits will be higher as exposure is reduced.
To get the best liquidity for index trading you may be better of dealing through a direct market access broker that offers on-exchange futures and options execution. This way you can see the order book and get a live overview of liquidity in the market place.
However, futures (trading through futures brokers) are a professional trading product and only available to clients that have sufficient experience and funds. For traders that do not qualify for a professional trading account liquidity issues are basically moot as traders that do not qualify as professional should not really be trading in the volumes and size that would require additional margin.
A great book to get more information on this is Flash Crash, by Liam Vaughan, which tells the story of Navinder Sarao AKA the Hound of Hounslow, a futures trader on the e-mini S&P. It talks in-depth about how liquidity in the indices market work
Index Trading Platform FAQs:
Yes, you can make money trading indices, but Index trading is a high risk. To successfully make money trading indices you will either have to invest in indices in the long term or call the market right in the short-term. It is worth keeping in mind that only around 25% of non-professional traders make money. but some are easier to trade than others.
Yes, you can compare the best brokers for trading volatility here.
Index brokers make money through fees and financing charges. Index broker costs can be broken down depending on how an index is traded.
The different types of index broker make money in these ways
- Futures index brokers – commission charge on a per lot basis
- Options index brokers – commission charged on a per lot basis
- CFD index brokers – the bid/offer spread is widened and overnight interest is charged on positions
- Spread Betting index brokers- the bid/offer spread is widened and overnight interest is charged on positions
- ETF index brokers – commission charge on buys and sells, plus an account maintenance charge
Here is a list of the most popular stock markets to trade with an index broker. You can read more about each specific index, the pros and cons of trading and what economic factors move the market by either clicking on the below index links or reading our guide on the top ten stock market indices for trading and why.